The alpha-2 Adrenergic Receptors (The Receptors)
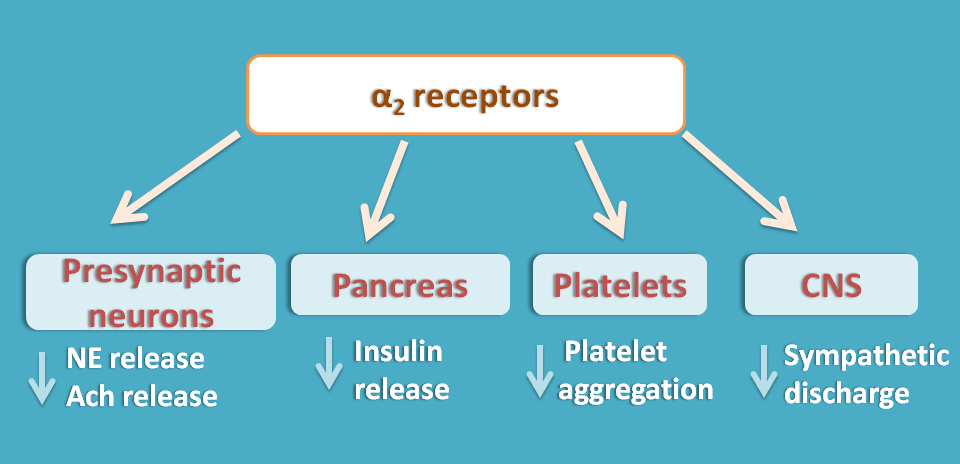
The different subtypes can coexist in some tissues, but one subtype normally predominates. There are three subtpyes of alpha 2 adrenoceptors 2A-C. The receptors are usually found presynaptically, where they inhibit the release of noradrenaline, and thus serve as an important receptor in the negative feedback control of noradrenaline release [ PMID: Postsynaptic alpha 2 receptors are located on liver cells, platelets, and the smooth muscle of blood vessels.
Activation of the receptors causes platelet aggregation [ PMID: Agonists of alpha 2 adrenergic receptors are frequently used in veterinary anaesthesia, where they affect sedation, muscle relaxation and analgesia through their effects on the CNS [ PMID: This entry represents the alpha 2A adrenoceptor.
By sequence By domain architecture. Add your annotation Add your annotation.
Alpha-2 Adrenergic Receptor Agonists: A Review of Current Clinical Applications
A study of the adrenotropic receptors. Subtypes of alpha 2-adrenoceptors: Ligand efficacy and potency at recombinant alpha2 adrenergic receptors: While the latter conclusion was subsequently shown to be incorrect it is now known to be noradrenaline , his receptor nomenclature and concept of two different types of dectors mechanisms for a single neurotransmitter , remains.
These concepts would revolutionise advances in pharmacotherapeutic research, allowing the selective design of specific molecules to target medical ailments rather than rely upon traditional research into the efficacy of pre-existing herbal medicines. G i and G s are linked to adenylyl cyclase. The result is that high levels of circulating epinephrine cause vasoconstriction.
Smooth muscle behavior is variable depending on anatomical location.
- The Beekman 1802 Heirloom Vegetable Cookbook: 100 Delicious Heritage Recipes from the Farm and Garden.
- Adrenergic receptor - Wikipedia.
- Alpha-2 adrenergic receptor;
- Wicked Women Whodunit.
- Private (Kindle Single).
- La réforme de la garde à vue (Droit privé et sciences criminelles) (French Edition).
One important note is the differential effects of increased cAMP in smooth muscle compared to cardiac muscle. Increased cAMP will promote relaxation in smooth muscle, while promoting increased contractility and pulse rate in cardiac muscle. Common or still receptor unspecified actions include:.
The former interacts with calcium channels of endoplasmic and sarcoplasmic reticulum , thus changing the calcium content in a cell.
- Existence in Black: An Anthology of Black Existential Philosophy.
- There was a problem providing the content you requested?
- Specific Drugs and Therapeutic Uses.
- Navigation menu!
- Adrenergic receptor?
- CV Pharmacology | Alpha-Adrenoceptor Agonists (α-agonists).
- Belleville Story - tome 1 - Avant Minuit (1) (French Edition)!
- Seiser & Kumli on California Juvenile Courts Practice and Procedure, 2012 Edition?
- .
This triggers all other effects, including a prominent slow after depolarizing current sADP in neurons. It causes vasoconstriction in many blood vessels , including those of the skin , gastrointestinal system , kidney renal artery [13] and brain. This decreases the effect of NE.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. History of catecholamine research. There was a subtype known as C, but it was found to be identical to one of the previously discovered subtypes. To avoid confusion, naming was continued with the letter D. Sympathin E and Sympathin I". American Journal of Physiology. The Journal of Physiology.
Alpha-2 Adrenergic Receptor Agonists: A Review of Current Clinical Applications
The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. Both epinephrine and norepinephrine activates both the alpha 1 and alpha 2 receptors. Presynaptic Alpha 2 Receptors Alpha 2 receptors also exist presynaptically associated with nerve terminals. Activation of these receptors inhibits the release of norepinephrine. Norepinephrine acts at presynaptic alpha 2 receptors to inhibit its own release. Associated with vascular smooth muscle are a large number of alpha 1 receptors relative to beta 2 receptors.
MECHANISM OF ACTION
Activation of these receptors by sympathetic nervous system transmission or drugs will result in vasoconstriction and an increase in peripheral resistance and systemic arterial blood pressure. Applications to Therapeutics Oral dosing of norepinephrine or epinephrine is not possible due to the rapid metabolism of catechol nucleus in gastrointestinal mucosa and liver. Therefore, these agents are given I.
Epinephrine is often used in combination local anesthetic agents to prolong the duration of anesthetic action. This would include articaine, bupivacaine or lidocaine. This combination is used because epinephrine can induce vasoconstriction thus limiting the diffusion of the local anesthetic from the site of injection.
This not only prolongs the actions of the local anesthetic but also to reduce the toxicity of the local anesthetic by limiting its systemic absorption. Lidocaine in toxic doses can produce cardiac arrthythmias and convulsions. Epinephrine can also be topically applied in surgical procedures to induce vasoconstriction and thus reduce blood loss. Epinephrine is used in the treatment of shock and in emergency situations related to bronchial asthma.
Clinical studies have shown that epinephrine blood levels increase following its intraoral administration. The risk of this increase is dependent on characteristics of the patient. For example, hypertensive patients or those with other cardiovascular disease or patients taking other drugs that affect sympathetic nervous system function are at higher risk than patients without these conditions.
Systemically absorbed epinephrine could also increase heart rate and exacerbate cardiac rhythm disturbances or myocardial ischemia. Learning Objectives Lecture II 1. Understand the pharmacologic actions and therapeutic actions of drugs that act at the beta 1 and beta 2 -adrenergic receptors as well as the alpha 1 -adrenergic receptor. Know the mechanism of action and effects of amphetamine and cocaine. Understand how the pressure of sympathomimetics alters the dental management of patients.
These agents can be divided into direct and indirect acting sympathomimetics.
Alpha-Adrenoceptor Agonists (α-agonists)
Direct acting agonists or antagonists can act at postsynaptic receptors. Indirect acting agonists release neurotransmitters from presynaptic nerve terminals to produce a sympathomimetic effect. Inhibition of the membrane uptake of catecholamines by drugs such as cocaine and tricyclic antidepressants produce a sympathomimetic effect. Inhibition of monoamine oxidase by drugs such as Tranylcypromine.
In congestive heart failure, the failing heart is not able to eject blood as efficiently as the normal heart. As a result there is a decrease in cardiac output which triggers a host of compensatory actions. These include fluid retention, vasoconstriction, an increase in peripheral vascular resistance, an increase in the levels of circulating catecholamines and tissue hypoxia.
Dopamine and dobutamine activate the myocardial beta 1 receptor and thus increase the force of contraction of the failing heart. This will result in an increase in cardiac output. These drugs are reserved for use in the acute management of heart failure. These agents have a higher affinity lower equilibrium dissociation constant for beta 2 receptors when compared to beta 1. Therefore, they selectively activate beta 2 receptors when compared to beta 1.
Airways dysfunction; bronchial asthma, chronic bronchitis, emphysema In airways dysfunction, beta 2 selective agonists relax airways thus decreasing airways resistance.
Premature labor In premature labor, the beta 2 selective agonists relax uterine smooth muscle. Drugs that relax uterine smooth muscle are referred to as tocolytic agents. Side effects related to dental practice 1. Xerostomia, with inhaler usage.
These structural modifications of the parent catecholamine nucleus result in drugs that are orally active and have longer plasma half-lives. However, these same modifications result in lower affinity for the receptor than do the endogenous agonists epinephrine or norepinephrine. There are two structural classes of alpha 1 agonists phenethylamines which are closely aligned in structure to epinephrine and the imidazolines, compounds structurally unrelated to epinephrine.
Levonordeferin is a phenyethylamine that has been used in dental practice in combination with local anesthetics.
Contributing signatures
Hypotension-to increase blood pressure during a surgical procedure where a general anesthetic has induced hypotension 2. Ophthalmic preparations-to induce mydrasis also in topical preparations for symptomatic release of eye irritation. Cough and cold preparations-Induces constriction of nasal mucosa decreases resistance to air flow.
