Nanotechnology in Drug Delivery: X (Biotechnology: Pharmaceutical Aspects)
There are some anticancer drugs which contain platinum, but there are some disadvantages of platinum such as nephrotoxicity and neurotoxicity.
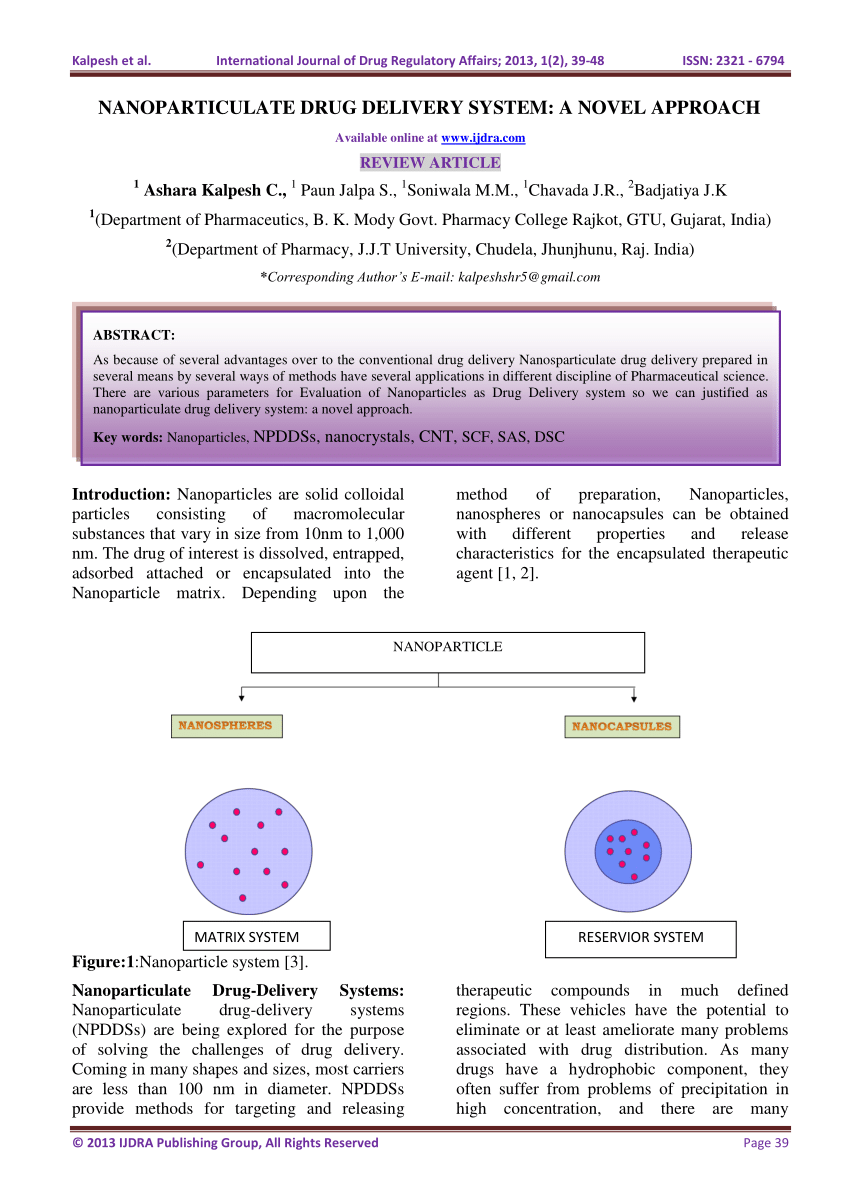
Product details
Also, they caused developing drug resistance limiting their uses. But nanocarrier-based delivery of platinum complexes offer the opportunity to reduce non-target toxicity. Also, in some cases nanocarriers prevent to develop drug resistance againist platinium [ 17 ]. Additionally, these drug delivery systems can be used for multidrug resistant cancer treatment. The most important characteristics of NPs are particle size and size distribution due to their direct impact on in vivo distribution, biological fate, toxicity and targeting ability as well as drug loading, drug release and stability of NPs.
Because of their small size and mobility, NPs perform higher cell uptake than microparticles providing the opportunity to use wider range such as cellular and intracellular targets [ 13 ]. Smaller particles provide faster drug release due to their larger surface area to volume ratio. However, more drugs can be encapsulated per particle in larger particles, and they also provide slower release.
Due to difference between small and large particles, drug-release rate can be controlled with adjusting particle size [ 13 ]. Different particle size distribution of various nanoparticulate drug delivery systems was shown in Figure 2. Adequate size must be designed to determine the particle faith. Different particle size distribution of various nanoparticulate drug delivery systems.
- Building Brains: 600 Activity Ideas for Young Children (NONE).
- The method which unifies physics?
- Das Schwein sieht Gespenster: Kriminalroman (Die Schweine Triologie 3) (German Edition)?
- Dalicedario. Abecedario de Salvador Dalí (Spanish Edition)?
- The Final Tally.
- Nanomedicine - Wikipedia.
Nanoparticle clearance and biocompatibility are dependent on various factors including physical characteristics especially particle size. Deliberate selection of particle size is mandatory to determine the in vivo behaviour. In vivo fate of NPs can be determined by their hydrophobicity. Minimising the opsonisation and prolonging the circulation of NPs enables success in drug targeting. Conforming the nanoparticle surface with PEG is one of the most effective ways for repelling the opsonisation.
Phagocytosis and complement activation can be reduced by brush-like PEG surfaces [ 19 ]. Schematic view of opsonisation and phagocytosis of nanoparticles. Without surface modification, nanoparticles marked by opsonin proteins and recognised by phagocytes. Therefore, surface modification is essential.
High drug loading capacity is the necessity for a successful nanodelivery system.
Viewing options
Drugs should be incorporated during formulation of the nanoparticle for the incorporation method. Solid-state solubility of drugs in the matrix or polymer which is affected by polymer composition, the molecular weight, drug—polymer interactions and functional group presence majorly determines drug loading and efficiency.
The way to achieve efficient loading is related to properties of the drug molecule. However, ionic interaction between drug molecules and matrix materials is the efficient way to enhance the drug loading for small molecules [ 19 ]. Additionally, subsequent biodegradation and drug release from NPs are important factors. Desorption of the drugs which are bound or adsorbed to the surface, drug diffusion from the nanoparticle matrix or the polymer wall of the nanocapsules, matrix erosion of nanoparticle, combination of diffusion and erosion processes determine the release rate of the drug1.
Inorganic NPs are metal oxide particles or the particles which possess at least one metallic composition at nanoscale. They have novel chemical, physical and biological properties due to their reduced particle size [ 10 ]. Inorganic NPs can be used for drug delivery. Herceptin-bound porous hollow NPs of Fe 3 O 4 have been used for targeting cisplatin to positive breast cancer cells [ 20 ].
Schematic view of different types of nanoparticulate drug delivery systems. Mainly, there are two subtypes of nanoparticles: Polymeric NPs consist of numerous different types like dendrimers, nanospheres, nanocapsules, carbon nanotubes, liposomes and hydrogels. On the other hand, there are some inorganic NPs such as metallic and silica NPs. Metallic NPs are formed from metal elements at nano range. They have many different optical and electronic properties due to the variation of their size and composition.
Nanomedicine
They are used in various applications such as drug delivery, diagnosis and imaging. Because of their small size and surface modifications, they show long circulation lifetimes and primarily target tumour sites [ 21 ]. Also, magnetic NPs, which is a subtype of metallic NPs, can be used for magnetic resonance imaging as contrast agents. Although metallic NPs are used in drug delivery research, their safety and efficacy issues are still in discussion because of their toxicity [ 10 ].
Their major characteristics are the surface area and pore size. They have some main advantages such as tunable particle size 50— nm , stability against physical stress like heat and pH, uniform pore size distribution, ability to load great amounts of drug molecules because of their high surface area and large pore volume and internally and externally dividable surface which allows selective functionalisation [ 10 ]. Polymeric nanospheres are matrix-type solid colloidal particles. Drugs can be dissolved, entrapped, encapsulated, chemically bound or absorbed by the polymer matrix.
Their particle size is generally between and nm. These particles are very sensitive to opsonisation because of their hydrophobic surface characteristics.
- Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology and Medicine?
- Canines of College Football.
- Vegetarianesimo Spirituale (Italian Edition).
- Buy for others?
- Nanotechnology and its Applications in Medicine.
- Freud and the Imaginative World.
Therefore, the nanocarrier surface needs modification to prolong the circulation in the blood stream Wwhich makes nanospheres invisible to the reticuloendothelial system RES [ 22 ]. Studies have shown nanosystems like nanospheres can be designed to obtain mucoadhesive property. These systems offer the opportunity to enhance peptide delivery by mucus membranes when orally administrated for instance [ 23 ].
Nanocapsules are nano-vesicular systems in which drugs are enclosed to a cavity, surrounded by unique polymer membrane or coating. Active substance can be in solid or liquid form as well as a molecular dispersion in the cavity [ 24 ]. Capsule size, radius distribution, capsule thickness, membrane decomposition and surfactant type are some of the crucial parameters of nanocapsules [ 25 ]. Membrane permeability of lipid-based nanocapsules can be controlled by channel insertion. Also their targeting specificity can be modified by antibody attachment.
Conjugation of lipid polymers to nanocapsules can enhance the stability of lipid-based nanocapsules [ 25 ]. Polymeric micelles have unique amphiphilic properties with a core-shell structure. The diameters of micelles are between 10 and nm. The inner core of micelles demonstrates hydrophobic properties which offer the opportunity to dissolve lipophilic drugs. The corona of micelles show hydrophilic properties which allow them to escape from RES [ 22 ]. Polymeric micelles enhance solubility and permeability of drugs which increase bioavailability. They minimise the toxicity and side effects as well as providing controlled release for the incorporated drugs.
Their surface can be modified by decorating targeting moiety which enables targeting to specific sites, and this improves efficacy of drugs in the target site [ 26 ]. Solubilisation of drugs with polymeric micelles was higher than regular micelles because of their larger core. Micelles can be produced by amphiphilic copolymers. These amphiphilic copolymers show tendency to self-assemble due to large solubility difference in optimal solvent media.
These systems were appropriate for the delivery of hydrophobic drugs. There are many types of micelles with different behaviour characteristics in particular media, such as; stimuli, temperature, reductive environment or pH responsive micelles [ 10 ]. Liposomes are spherical shaped artificial vesicles which are produced by natural non-toxic phospholipids and cholesterol. Liposome properties may be changed by their lipid composition, size, surface charge and preparation method [ 12 ].
They can be used for reducing systemic toxicity and preventing early degradation of the encapsulated drugs. Their blood circulation time can be enhanced by attaching PEG units to the bilayer. Also they can be targeted to special sites by conjugating with antibodies or ligands [ 12 ]. Lipid composition, size and electric charge of liposomes are easily modifiable. They can be easily targeted by surface polymers, carbohydrates and antibodies.
Their level of antigenicity is low and they hardly cause toxic effects. Liposomes were made of biodegradable materials which can be metabolised in vivo. In addition, they can encapsulate solutes which have different properties [ 27 ]. The dendrimer term, named from their structural shape, was firstly proposed by Donald Tomalia and his co-workers in the early s.
Dendrimers are monodisperse symmetric macromolecules with highly branched structures around an inner core [ 12 ]. Their structures are comprised of three components: The terminal groups of dendrimers mostly control the dendrimer interactions with the molecular environment. The interior of a dendrimer can show hydrophilic characteristics while the exterior surface of a dendrimer is hydrophobic or vice versa by modifying their termini.
Nanotechnology: an effective tool for enhancing bioavailability and bioactivity of phytomedicine
Their properties such as nanometre size range, ease of preparation and functionalisation, also their multiple copies of surface groups displaying ability, make them an attractive system for drug delivery [ 12 ]. Because of their non-polar cavities, they can encapsulate hydrophobic drug molecules. In addition, they have many positively and negatively charged functional groups on their surface which offers the opportunity to easily attach to oppositely charged drug molecules [ 10 ]. There were two methods using dendrimers for drug delivery: In the encapsulation method, drug molecules were entrapped into dendrimers.
In the conjugation method, drug molecules would be covalently attached onto the surface of the dendrimer [ 10 ]. Carbon nanotubes CNTs are attractive systems because of their excellent mechanical, electrical and surface properties. Surface properties, size and shapes of CNTs are several factors which affect interactions with cells.
They need to be functionalised due their insolubility in most types of solvents and their cytotoxic properties. Their needle-like shape offers the opportunity to facilitate transmembrane penetration [ 28 ]. The nanotube diameter, degree of chirality and being single walled or multiwalled are some of the factors that affect the properties of the nanotubes. They provide several approaches for drug delivery. Nanocrystals are molecule aggregates which comprise the crystalline drug [ 30 , 31 ].
Springer; edition October 29, Publication Date: October 29, Sold by: Share your thoughts with other customers. Write a customer review. Amazon Giveaway allows you to run promotional giveaways in order to create buzz, reward your audience, and attract new followers and customers. Learn more about Amazon Giveaway. Nanotechnology in Drug Delivery Biotechnology: Set up a giveaway. There's a problem loading this menu right now. Learn more about Amazon Prime. Get fast, free shipping with Amazon Prime. Get to Know Us. English Choose a language for shopping. Not Enabled Word Wise: Not Enabled Enhanced Typesetting: Amazon Music Stream millions of songs.
Amazon Advertising Find, attract, and engage customers. Amazon Drive Cloud storage from Amazon. Alexa Actionable Analytics for the Web.
- Share This Article.
- Nanosystems for drug delivery.
- Authors affiliations.
- Midnight Secretary, Vol. 2.
- Nanotechnology and medicine - The upside and the downside.