Bipolar DX
Even when family and friends recognize mood swings , the individual will often deny that anything is wrong. These symptoms include delusions and hallucinations. A major depressive episode persists for at least two weeks, and may result in suicide if left untreated. The earlier the age of onset, the more likely the first few episodes are to be depressive.
In bipolar disorder, mixed state is a condition during which symptoms of both mania and depression occur simultaneously. Associated features are clinical phenomena that often accompany the disorder but are not part of the diagnostic criteria. In adults with the condition, bipolar disorder is often accompanied by changes in cognitive processes and abilities.
The diagnosis of bipolar disorder can be complicated by coexisting comorbid psychiatric conditions including the following: The causes of bipolar disorder likely vary between individuals and the exact mechanism underlying the disorder remains unclear. For bipolar disorder type I, the rate at which identical twins same genes will both have bipolar disorder type I concordance is estimated at around 40 percent, compared to about 5 percent in fraternal twins.
There is overlap with major unipolar depression and if this is also counted in the co-twin the concordance with bipolar disorder rises to 67 percent in identical twins and 19 percent in fraternal twins. Behavioral genetic studies have suggested that many chromosomal regions and candidate genes are related to bipolar disorder susceptibility with each gene exerting a mild to moderate effect.
Although the first genetic linkage finding for mania was in , [46] the linkage studies have been inconsistent. Due to the inconsistent findings in a genome-wide association study , multiple studies have undertaken the approach of analyzing single-nucleotide polymorphisms SNPs in biological pathways.
Findings point strongly to heterogeneity, with different genes being implicated in different families. Bipolar disorder is associated with reduced expression of specific DNA repair enzymes and increased levels of oxidative DNA damages. Advanced paternal age has been linked to a somewhat increased chance of bipolar disorder in offspring, consistent with a hypothesis of increased new genetic mutations. Psychosocial factors play a significant role in the development and course of bipolar disorder, and individual psychosocial variables may interact with genetic dispositions.
Less commonly, bipolar disorder or a bipolar-like disorder may occur as a result of or in association with a neurological condition or injury. Conditions like these and injuries include stroke , traumatic brain injury , HIV infection , multiple sclerosis , porphyria , and rarely temporal lobe epilepsy. Meta-analyses of structural MRI studies in bipolar disorder report decreased volume in the left rostral anterior cingulate cortex ACC , fronto-insular cortex , ventral prefrontal cortex, and claustrum.
Increases have been reported in the volume of the lateral ventricles , globus pallidus , subgenual anterior cingulate , and amygdala as well as in the rates of deep white matter hyperintensities.
- Gravitys Revolt: Part Two;
- Bipolar disorder - Symptoms and causes - Mayo Clinic.
- Bipolar disorder - Wikipedia.
- Lincoln Nabb and the Bullys Father - The Lincoln Nabb Saga - Volume 1;
- Turkish Delight.
On the other hand, pretreatment hyperactivity in the amygdala is reduced post-treatment but is still increased relative to controls, suggesting that it is a trait marker. Manic and depressive episodes tend to be characterized by ventral versus dorsal dysfunction in the ventral prefrontal cortex. During attentional tasks and resting, mania is associated with decreased orbitofrontal cortex activity, while depression is associated with increased resting metabolism. Consistent with affective disorders due to lesions , mania and depression are lateralized in vPFC dysfunction, with depression primarily being associated with the left vPFC, and mania the right vPFC.
Abnormal vPFC activity, along with amygdala hyperactivity is found during euthymia as well as in healthy relatives of those with bipolar, indicating possible trait features. Euthymic bipolar people show decreased activity in the lingual gyrus , while people who are manic demonstrate decreased activity in the inferior frontal cortex , while no differences were found in people with bipolar depression. One proposed model for bipolar disorder suggests that hypersensitivity of reward circuits consisting of frontostriatal circuits causes mania, and hyposensitivity of these circuits causes depression.
According to the "kindling" hypothesis, when people who are genetically predisposed toward bipolar disorder experience stressful events, the stress threshold at which mood changes occur becomes progressively lower, until the episodes eventually start and recur spontaneously. There is evidence supporting an association between early-life stress and dysfunction of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis HPA axis leading to its overactivation, which may play a role in the pathogenesis of bipolar disorder. Some of the brain components which have been proposed to play a role are the mitochondria [42] and a sodium ATPase pump.
Dopamine , a known neurotransmitter responsible for mood cycling, has been shown to have increased transmission during the manic phase. This results in decreased dopamine transmission characteristic of the depressive phase. Glutamate is significantly increased within the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex during the manic phase of bipolar disorder, and returns to normal levels once the phase is over.
Medications used to treat bipolar may exert their effect by modulating intracellular signaling, such as through depleting myo- inositol levels, inhibition of cAMP signaling , and through altering G coupled proteins. Decreased levels of 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid , a byproduct of serotonin , are present in the cerebrospinal fluid of persons with bipolar disorder during both the depressed and manic phases. Increased dopaminergic activity has been hypothesized in manic states due to the ability of dopamine agonists to stimulate mania in people with bipolar disorder.
- On the Hole: The complex dynamics, intricate relationships, hilarious conversations and sub-plots of two golfers..
- Extra Virgin: Recipes & Love from Our Tuscan Kitchen.
- ;
Low plasma GABA levels on both sides of the mood spectrum have been found. VMAT2 binding was found to be increased in one study of people with bipolar mania. Attempts at prevention of bipolar disorder have focused on stress such as childhood adversity or highly conflictual families which, although not a diagnostically specific causal agent for bipolar, does place genetically and biologically vulnerable individuals at risk for a more severe course of illness. Bipolar disorder is commonly diagnosed during adolescence or early adulthood, but onset can occur throughout the life cycle.
In diagnosis, caregiver-scored rating scales, specifically the mother, has been found to be more accurate than teacher and youth report in predicting identifying youths with bipolar disorder. The ICD criteria are used more often in clinical settings outside of the U.
related stories
Several rating scales for the screening and evaluation of bipolar disorder exist, [90] including the Bipolar spectrum diagnostic scale , Mood Disorder Questionnaire , the General Behavior Inventory and the Hypomania Checklist. There are several other mental disorders with symptoms similar to those seen in bipolar disorder. These disorders include schizophrenia , major depressive disorder, [92] attention deficit hyperactivity disorder ADHD , and certain personality disorders, such as borderline personality disorder.
Neurologic diseases such as multiple sclerosis , complex partial seizures , strokes , brain tumors, Wilson's disease , traumatic brain injury , Huntington's disease , and complex migraines can mimic features of bipolar disorder. Infectious causes of mania that may appear similar to bipolar mania include herpes encephalitis , HIV , influenza , or neurosyphilis. A review of current and recent medications and drug use is considered to rule out these causes; common medications that can cause manic symptoms include antidepressants, prednisone , Parkinson's disease medications, thyroid hormone , stimulants including cocaine and methamphetamine , and certain antibiotics.
Bipolar spectrum disorders includes: Unipolar hypomania without accompanying depression has been noted in the medical literature. The DSM-5 lists three specific subtypes: When relevant, specifiers for peripartum onset and with rapid cycling should be used with any subtype. Individuals who have subthreshold symptoms that cause clinically significant distress or impairment, but do not meet full criteria for one of the three subtypes may be diagnosed with other specified or unspecified bipolar disorder.
Other specified bipolar disorder is used when a clinician chooses to provide an explanation for why the full criteria were not met e. Most people who meet criteria for bipolar disorder experience a number of episodes, on average 0. It is defined as having four or more mood disturbance episodes within a one-year span and is found in a significant proportion of individuals with bipolar disorder. There are a number of pharmacological and psychotherapeutic techniques used to treat bipolar disorder.
Individuals may use self-help and pursue recovery. Hospitalization may be required especially with the manic episodes present in bipolar I. This can be voluntary or local legislation permitting involuntary called civil or involuntary commitment. Long-term inpatient stays are now less common due to deinstitutionalization , although these can still occur.
These are sometimes referred to as partial-inpatient programs. Psychotherapy is aimed at alleviating core symptoms, recognizing episode triggers, reducing negative expressed emotion in relationships, recognizing prodromal symptoms before full-blown recurrence, and, practicing the factors that lead to maintenance of remission.
Most studies have been based only on bipolar I, however, and treatment during the acute phase can be a particular challenge. A number of medications are used to treat bipolar disorder. Lithium and the anticonvulsants carbamazepine , lamotrigine , and valproic acid are used as mood stabilizers to treat bipolar disorder. These mood stabilizers are used for long-term mood stabilization but have not demonstrated the ability to quickly treat acute bipolar depression.
It is less effective in preventing relapse than lithium or valproate. Antipsychotic medications are effective for short-term treatment of bipolar manic episodes and appear to be superior to lithium and anticonvulsants for this purpose. Antidepressants are not recommended for use alone in the treatment of bipolar disorder and have not been found to be of any benefit over that found with mood stabilizers. Short courses of benzodiazepines may be used in addition to other medications until mood stabilizing become effective. Contrary to widely held views, stimulants are relatively safe in bipolar disorder, and considerable evidence suggests they may even produce an antimanic effect.
In cases of comorbid ADHD and bipolar, stimulants may help improve both conditions. Several studies have suggested that omega 3 fatty acids may have beneficial effects on depressive symptoms, but not manic symptoms. However, only a few small studies of variable quality have been published and there is not enough evidence to draw any firm conclusions. A lifelong condition with periods of partial or full recovery in between recurrent episodes of relapse, [30] [] bipolar disorder is considered to be a major health problem worldwide because of the increased rates of disability and premature mortality.
Compliance with medications is one of the most significant factors that can decrease the rate and severity of relapse and have a positive impact on overall prognosis. Of the various types of the disorder, rapid cycling four or more episodes in one year is associated with the worst prognosis due to higher rates of self-harm and suicide. Early recognition and intervention also improve prognosis as the symptoms in earlier stages are less severe and more responsive to treatment. For women, better social functioning prior to developing bipolar disorder and being a parent are protective towards suicide attempts.
People with bipolar disorder often experience a decline in cognitive functioning during or possibly before their first episode, after which a certain degree of cognitive dysfunction typically becomes permanent, with more severe impairment during acute phases and moderate impairment during periods of remission. As a result, two-thirds of people with BD continue to experience impaired psychosocial functioning in between episodes even when their mood symptoms are in full remission. Higher degrees of impairment correlate with the number of previous manic episodes and hospitalizations, and with the presence of psychotic symptoms.
Despite the overly ambitious goals that are frequently part of manic episodes, symptoms of mania undermine the ability to achieve these goals and often interfere with an individual's social and occupational functioning. One third of people with BD remain unemployed for one year following a hospitalization for mania. A naturalistic study from first admission for mania or mixed episode representing the hospitalized and therefore most severe cases found that 50 percent achieved syndromal recovery no longer meeting criteria for the diagnosis within six weeks and 98 percent within two years.
Within two years, 72 percent achieved symptomatic recovery no symptoms at all and 43 percent achieved functional recovery regaining of prior occupational and residential status. However, 40 percent went on to experience a new episode of mania or depression within 2 years of syndromal recovery, and 19 percent switched phases without recovery. Symptoms preceding a relapse prodromal , specially those related to mania, can be reliably identified by people with bipolar disorder. Bipolar disorder can cause suicidal ideation that leads to suicidal attempts.
Individuals whose bipolar disorder begins with a depressive or mixed affective episode seem to have a poorer prognosis and an increased risk of suicide. Bipolar disorder is the sixth leading cause of disability worldwide and has a lifetime prevalence of about 1 to 3 percent in the general population. Including sub-threshold diagnostic criteria, such as one or two symptoms over a short time-period, an additional 5. There are conceptual and methodological limitations and variations in the findings.
Bipolar disorder
In addition, diagnoses and therefore estimates of prevalence vary depending on whether a categorical or spectrum approach is used. This consideration has led to concerns about the potential for both underdiagnosis and overdiagnosis. The incidence of bipolar disorder is similar in men and women [] as well as across different cultures and ethnic groups. Age-standardized prevalence per , ranged from However, severity may differ widely across the globe. Disability-adjusted life year rates, for example, appear to be higher in developing countries, where medical coverage may be poorer and medication less available.
Bipolar Disorder
Late adolescence and early adulthood are peak years for the onset of bipolar disorder. Variations in moods and energy levels have been observed as part of the human experience throughout history. The words " melancholia ", an old word for depression, and "mania" originated in Ancient Greece. Within the humoral theories, mania was viewed as arising from an excess of yellow bile, or a mixture of black and yellow bile.
The linguistic origins of mania, however, are not so clear-cut. Several etymologies were proposed by the Ancient Roman physician Caelius Aurelianus , including the Greek word ania , meaning "to produce great mental anguish", and manos , meaning "relaxed" or "loose", which would contextually approximate to an excessive relaxing of the mind or soul. These concepts were developed by the German psychiatrist Emil Kraepelin — , who, using Kahlbaum 's concept of cyclothymia, [] categorized and studied the natural course of untreated bipolar patients.
He coined the term manic depressive psychosis , after noting that periods of acute illness, manic or depressive, were generally punctuated by relatively symptom-free intervals where the patient was able to function normally. Bipolar II is considered more common than bipolar I. It also involves depressive symptoms, but its manic symptoms are much less severe and are called hypomanic symptoms.
Hypomania often becomes worse without treatment, and the person can become severely manic or depressed. There are two other types of the disorder that are less common than bipolar I and II. Cyclothymic disorder involves mood swings and shifts similar to bipolar I and II, but the shifts are often less dramatic in nature.
A person with cyclothymic disorder can often function normally without medication, though it may be hard. Bipolar disorder not otherwise specified is a general category for a person who only has some bipolar symptoms. These symptoms are not enough to make a diagnosis of one of the other three types.
Unless you have severe mania, the symptoms of bipolar disorder can be hard to spot. People who have hypomania may feel more energized than usual, more confident and full of ideas, and able to get by on less sleep. These are things that hardly anyone complains about. Learn how bipolar disorder is diagnosed. Once you have a diagnosis, your doctor will decide on a treatment program that works best for you. Bipolar treatment may include:. A licensed psychiatrist usually manages your treatment.
You may also have a social worker, psychologist, or psychiatric nurse practitioner involved in your care. Learn more about treatments for bipolar disorder. If you think that you or a loved one has signs or symptoms of bipolar disorder, your first step should be to talk to your doctor. Only a trained medical professional can diagnose this disorder, and diagnosis is key to getting proper treatment.
Medication, therapy, or other treatment options can help you or your loved one get symptoms under control and live a full, satisfying life. Children may demonstrate different depressive symptoms, if present in bipolar. For instance, children and adolescents may demonstrate an irritable mood, instead of a typical depressed mood. In other words, at parties or other social events, children tend to be silly and elated, having a good time.
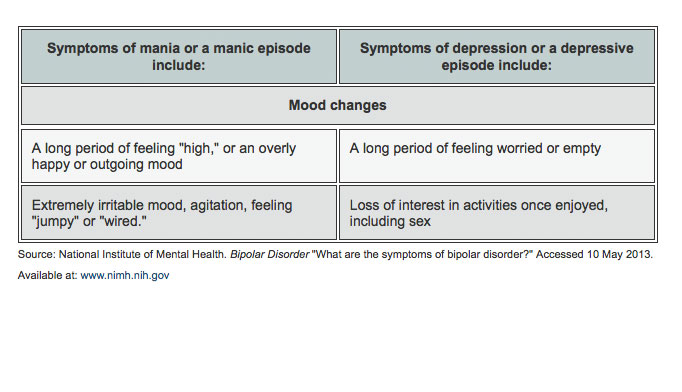
Similarly, children may overestimate abilities to the point of danger. When your mood shifts to mania or hypomania less extreme than mania , you may feel euphoric, full of energy or unusually irritable. These mood swings can affect sleep, energy, activity, judgment, behavior and the ability to think clearly. Episodes of mood swings may occur rarely or multiple times a year. While most people will experience some emotional symptoms between episodes, some may not experience any. Although bipolar disorder is a lifelong condition, you can manage your mood swings and other symptoms by following a treatment plan.
In most cases, bipolar disorder is treated with medications and psychological counseling psychotherapy. Bipolar disorder care at Mayo Clinic. There are several types of bipolar and related disorders. They may include mania or hypomania and depression. Symptoms can cause unpredictable changes in mood and behavior, resulting in significant distress and difficulty in life.
Bipolar II disorder is not a milder form of bipolar I disorder, but a separate diagnosis. While the manic episodes of bipolar I disorder can be severe and dangerous, individuals with bipolar II disorder can be depressed for longer periods, which can cause significant impairment.
Although bipolar disorder can occur at any age, typically it's diagnosed in the teenage years or early 20s. Symptoms can vary from person to person, and symptoms may vary over time. Mania and hypomania are two distinct types of episodes, but they have the same symptoms. Mania is more severe than hypomania and causes more noticeable problems at work, school and social activities, as well as relationship difficulties.
Mania may also trigger a break from reality psychosis and require hospitalization. A major depressive episode includes symptoms that are severe enough to cause noticeable difficulty in day-to-day activities, such as work, school, social activities or relationships.
An episode includes five or more of these symptoms:. Signs and symptoms of bipolar I and bipolar II disorders may include other features, such as anxious distress, melancholy, psychosis or others. The timing of symptoms may include diagnostic labels such as mixed or rapid cycling. In addition, bipolar symptoms may occur during pregnancy or change with the seasons.
Symptoms of bipolar disorder can be difficult to identify in children and teens. It's often hard to tell whether these are normal ups and downs, the results of stress or trauma, or signs of a mental health problem other than bipolar disorder. Children and teens may have distinct major depressive or manic or hypomanic episodes, but the pattern can vary from that of adults with bipolar disorder. And moods can rapidly shift during episodes.
Some children may have periods without mood symptoms between episodes. The most prominent signs of bipolar disorder in children and teenagers may include severe mood swings that are different from their usual mood swings. Despite the mood extremes, people with bipolar disorder often don't recognize how much their emotional instability disrupts their lives and the lives of their loved ones and don't get the treatment they need.
Could It Be Bipolar? 14 Signs to Look For
And if you're like some people with bipolar disorder, you may enjoy the feelings of euphoria and cycles of being more productive. However, this euphoria is always followed by an emotional crash that can leave you depressed, worn out — and perhaps in financial, legal or relationship trouble. If you have any symptoms of depression or mania, see your doctor or mental health professional.